Latest news
Researchers from Beijing Forestry University's School of Information Science (School of Artificial Intelligence) have achieved significant progress in document-level relation extraction, a core natural language processing task. The study, led by young faculty member Yan Rongen, has been published in IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, a top-tier journal (CCF A-class, IF=10.4) in artificial intelligence and data engineering.
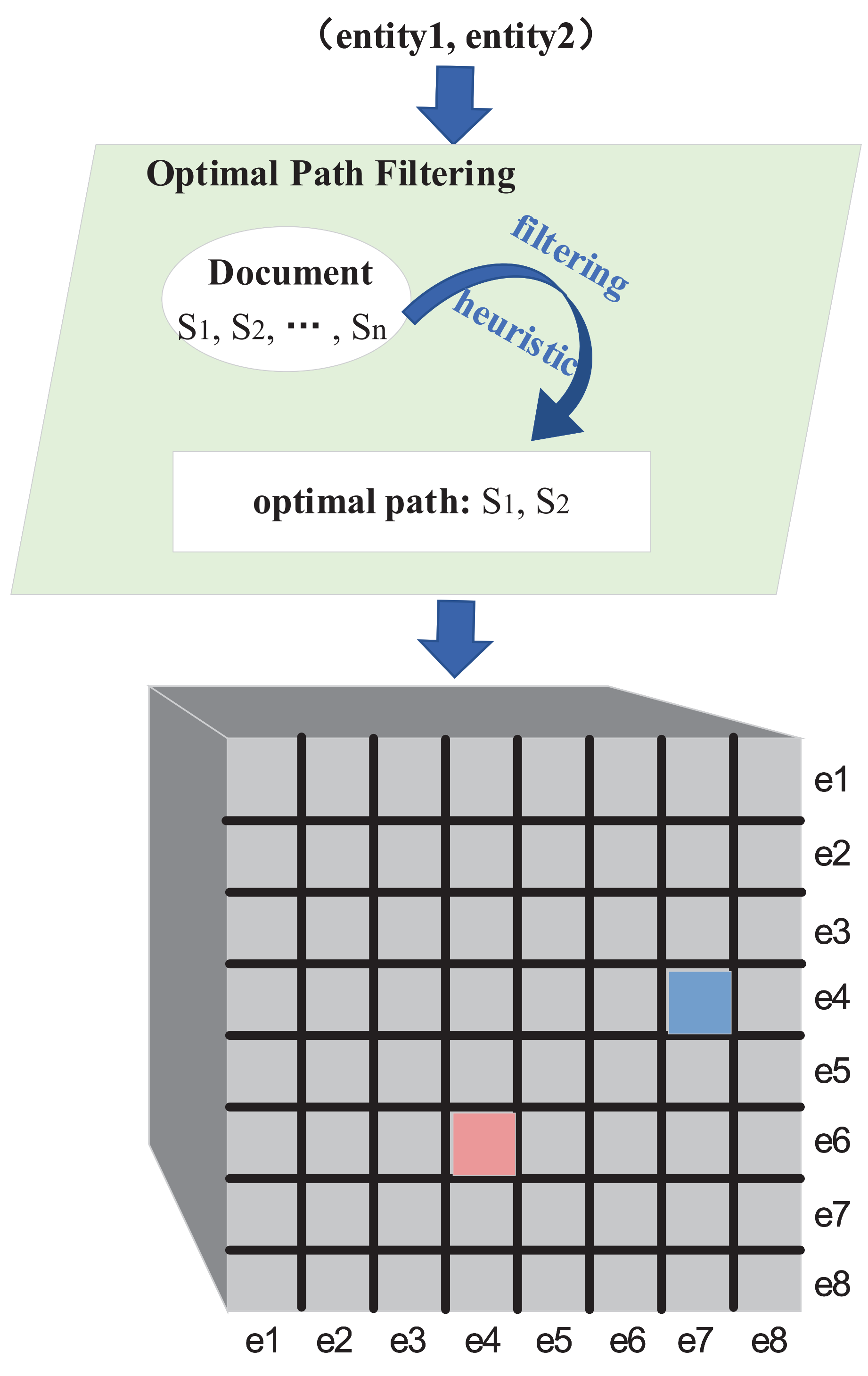
Document-level relation extraction (RE) aims to determine the relations between entities scattered across different sentences through reading and reasoning. Existing methods use semantic segmentation to obtain global information among triples by analyzing entity-level matrices. However, complete document input may introduce certain interference, making it challenging to express the underlying relationships. To address this, we propose a novel approach introducing a low-entity redundancy feature map, achieved by removing certain entities. The proposed optimal path filtering (OPF) selects entity-related sentences using heuristic rules and formulates sentence selection as a set cover problem, solved via backtracking pruning. U-Net is then applied to obtain global features. Our experiment achieves state-of-the-art results on two common document-level RE datasets, Re-DocRED and CDR, outperforming previous methods.
The paper's co-first authors are Yan Rongen from BFU and Professor Dang Depeng from Beijing Normal University. The research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(BLX202356), Central University Excellent Youth Team Project(QNTD202504) and other funding projects.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2025.3607566
Written by Yan Rongen
Tanslated and edited by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang












