Latest news
Recently, Fan Xin, a youth teacher at the School of Information Science and Technology, published an academic paper “CB-DSL: Communication-efficient and Byzantine-robust Distributed Swarm Learning on Non-i.i.d. Data" on "IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking", a top journal in the field of cognitive communications and Networking. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the first author. The journal is referred to as "IEEE TCCN" with an impact factor of 8.6 in 2023.
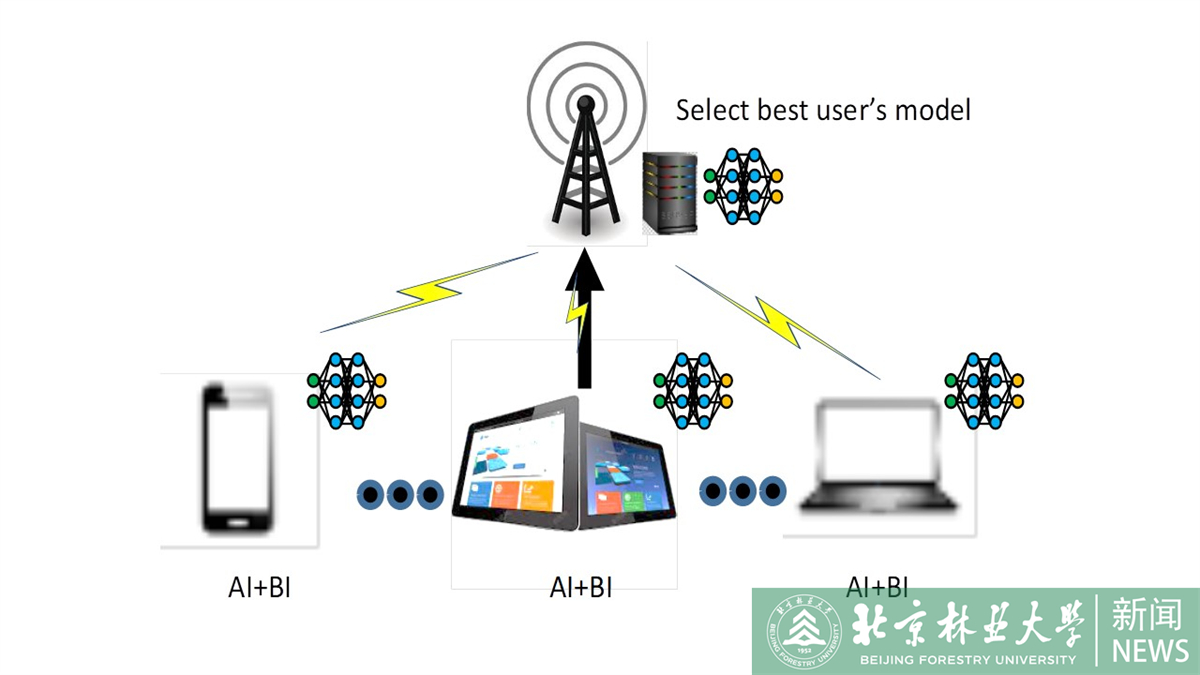
The valuable data collected by IoT devices together with the resurgence of machine learning (ML) stimulate the latest trend of artificial intelligence (AI) at the edge. However, traditional ML and recent federated learning (FL) face major challenges including communication bottleneck, data heterogeneity, and security concerns in edge IoT. Meanwhile, the swarm nature of IoT systems is overlooked by most existing literature, which calls for new designs of distributed learning algorithms. Inspired by the success of biological intelligence (BI) of gregarious organisms, we propose a novel edge learning approach for swarm IoT, called communication-efficient and Byzantine-robust distributed swarm learning (CB-DSL), through a holistic integration of AI-enabled stochastic gradient descent and BI-enabled particle swarm optimization. To deal with the non-i.i.d. data issues and Byzantine attacks, a small amount of global data samples are introduced in CB-DSL and shared among IoT workers, which alleviates the local data heterogeneity effectively and enables to fully utilize the exploration-exploitation mechanism of swarm intelligence. Our convergence analysis theoretically demonstrates that the CB-DSL is superior to the standard FL with better convergence behavior. We also evaluate the model divergence of CB-DSL by deriving its upper bound, which measures the effectiveness of the introduction of the globally shared dataset.
It is reported that this is the first attempt to use the respective algorithm-based advantages of AI and BI to improve the performance of distributed learning systems and give theoretical analysis of the research work, providing potential solutions for the application of distributed learning in large-scale intelligent Internet of Things scenarios, and promoting the further development of edge AI.
Paper link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10242235/










