Latest news
Professor Cheng Pengle's team from the School of Technology, Beijing Forestry University, has made a breakthrough in predicting global forest wildfire risks. By introducing an innovative data sampling approach rooted in information theory and developing SimFAN, a wildfire risk prediction model leveraging an enhanced Transformer framework, the research offers fresh insights into spatiotemporal wildfire patterns. The study entitled "Unveiling Spatiotemporal Patterns of Wildfire Risk: A Transformer-Based Earth System Analysis", was published in Climate Dynamics, a prominent journal in meteorology and atmospheric sciences with a 5-year impact factor of 4.4.
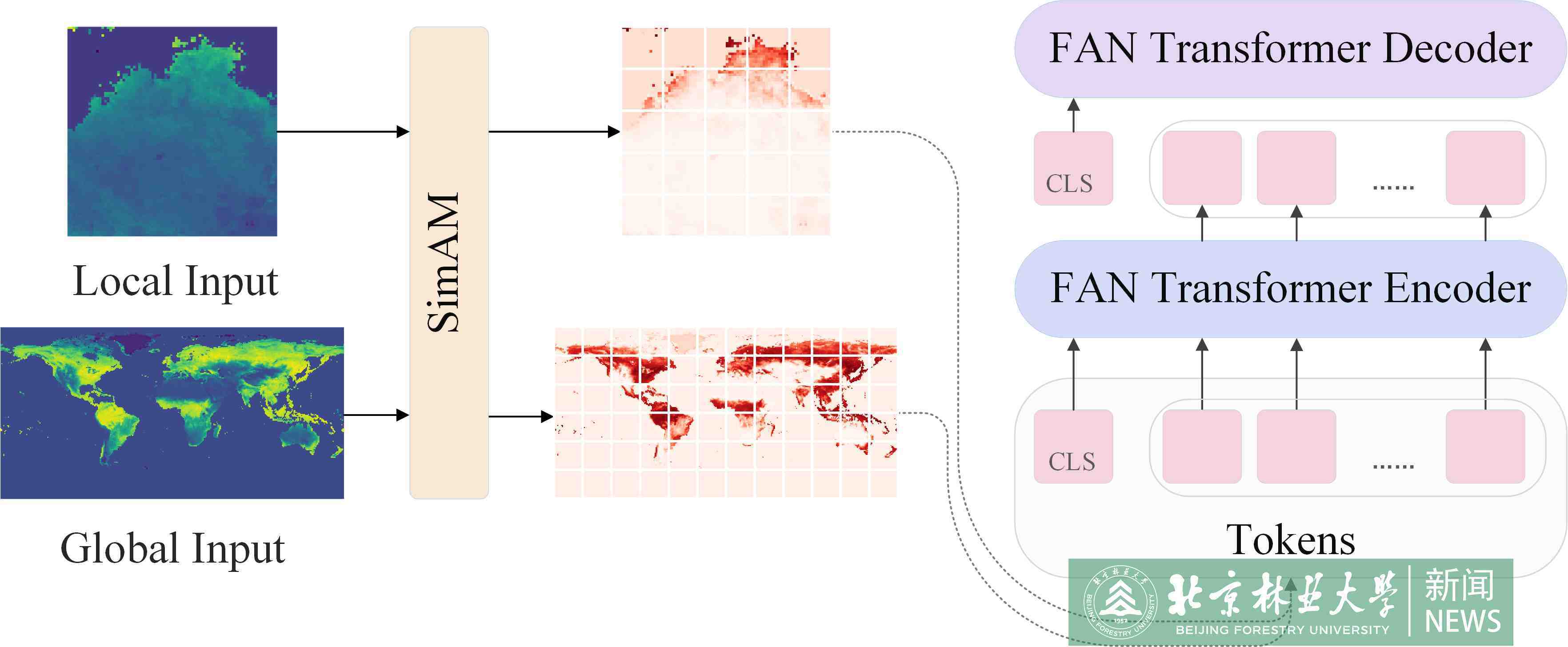
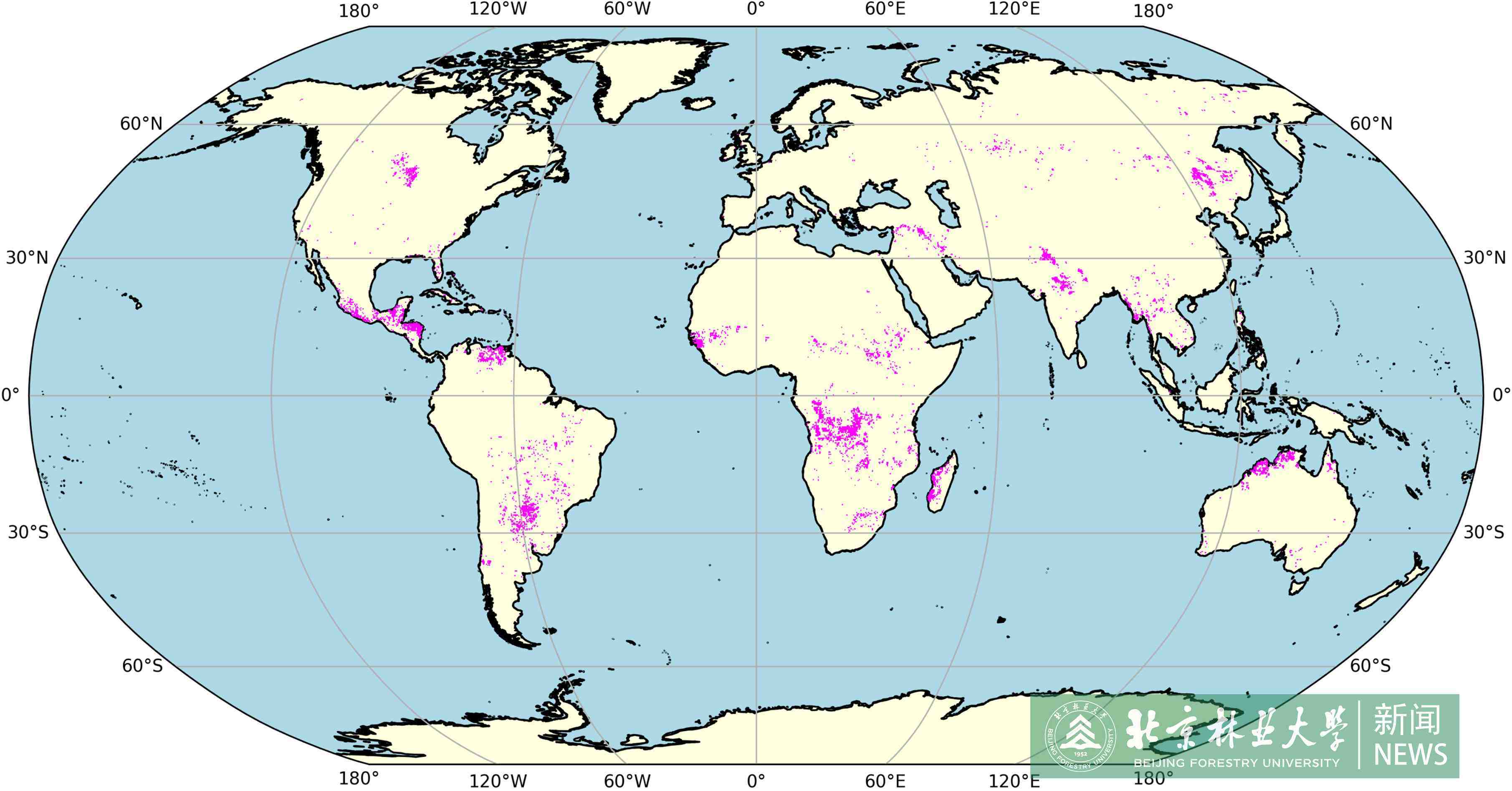
Wildfires profoundly influence ecosystems, human societies, and economic activities as a global phenomenon. The continuing climate change increases the frequency and intensity of wildfire, resulting in urgent needs in searching for better fire management strategies. This paper aims to pave a pathway towards meeting this challenge through accurately predicting spatiotemporal pattern of global wildfire risk, using an improved Transformer model that integrates information theory and full-attention mechanisms. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SimAM modulated Full Attention Network shows superior performances in terms of Accuracy, Recall, and Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve. Furthermore, new discoveries based on the model find out that the wildfire risk in the northern forest region of Australia is influenced by the seasonality of the climate in North America and the Pacific and the dry winter climate in the Canadian region, illuminating the intricate relationship between the global climate and regional wildfire risk. These findings provide new tools and knowledges for understanding the mechanisms in global wildfire risk.
Zhu Jiankai, a graduate student at the School of Technology at BFU is the first author of the paper. Professor Cheng Pengle served as the corresponding author, with Researcher Wang Mingyu from the Chinese Academy of Forestry's Research Institute of Forest Ecology, Environment, and Nature Conservation as the co-corresponding author.
The research was supported by the National Key R&D Program (2023YFD2202001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171797). This study offers innovative theoretical and technical insights into global wildfire prediction and management. These findings hold substantial value in advancing forest ecosystem management and strengthening wildfire prevention and control on a global scale.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-024-07481-y
Written by Zhu Jiankai, Cheng Pengle
Translated and edited by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang










