Latest news
The Machine Vision and Artificial Intelligence (MV&AI) Laboratory at the School of Engineering, Beijing Forestry University, has recently made strides in hyperspectral non-destructive monitoring. Their study, titled "Evaluation and process monitoring of jujube hot air drying using hyperspectral imaging technology and deep learning for quality parameters", has been published in Food Chemistry (IF=8.5), a leading journal in agricultural and forestry sciences.
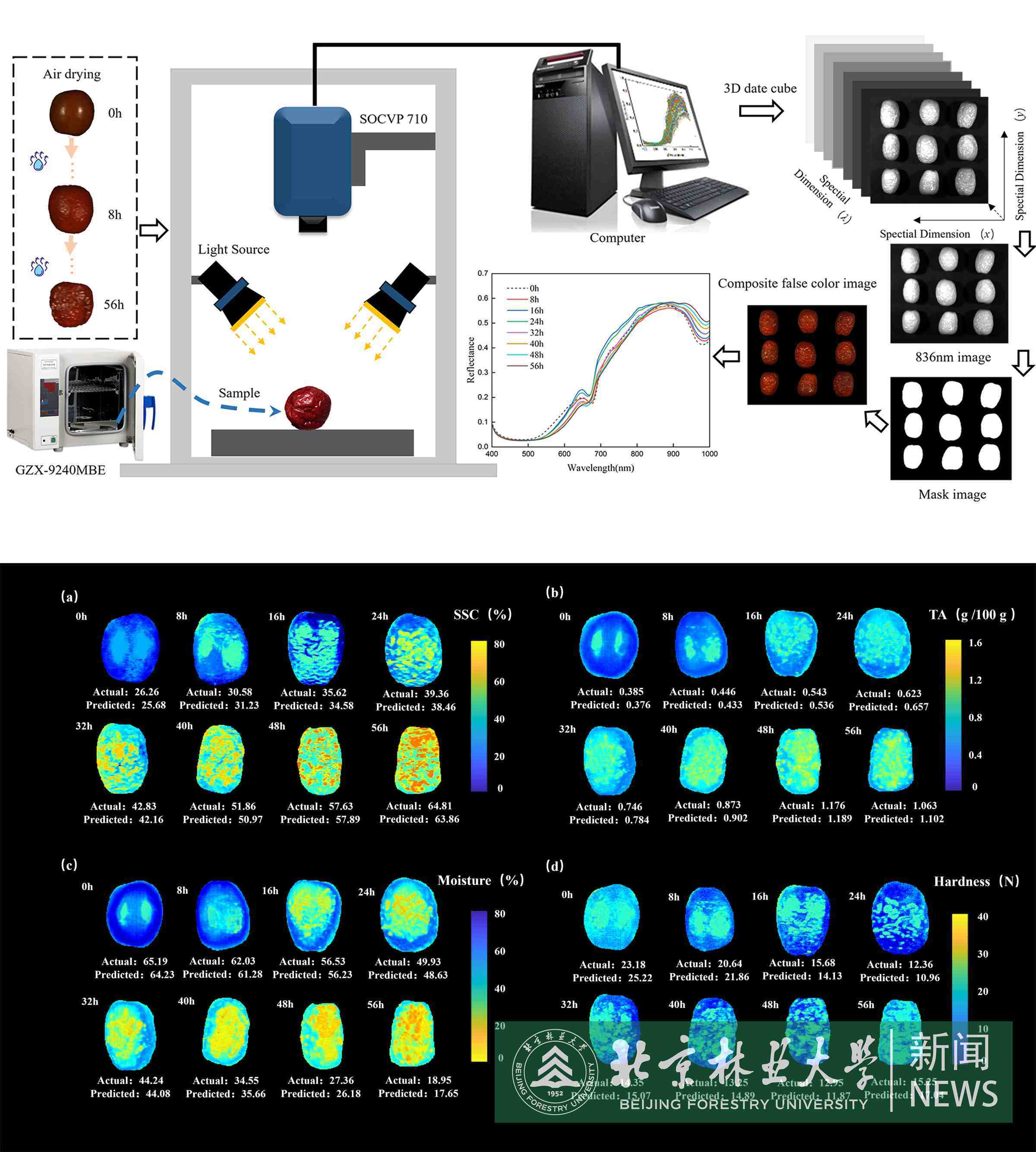
Drying is a fundamental process in food processing, where precise monitoring of drying quality attributes is imperative to achieve an acceptable final product. Timely and effective detection of quality attributes during drying control is essential for enhancing the quality of fruit processing. Consequently, this study aims to employ hyperspectral imaging technology for the non-destructive monitoring of soluble solids content (SSC), titratable acidity (TA), moisture, and hardness in jujubes during hot air drying. Quality parameters were measured at drying temperatures of 55 °C, 60 °C, and 65 °C. A deep learning model (CNN_BiLSTM_SE) was developed, incorporating a convolutioyounal neural network (CNN), bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM), and a squeeze-and-excitation (SE) attention mechanism. The performance of PLSR, SVR, and CNN_BiLSTM_SE was compared using different preprocessing methods (MSC, Baseline, and MSC_1st). The CNN_BiLSTM_SE model, optimized for hyperparameters, outperforms PLSR and SVR in predicting jujube quality attributes. Subsequently, these best prediction models were used to predict quality attributes at the pixel level for jujube, enabling the visualization of the Spatio-temporal distribution of these parameters at different drying stages.
Liu Quancheng, a doctoral candidate from the School of Engineering, served as the paper's first author, with Associate Professor Fan Shuxiang and Professor Yan Lei as co-corresponding authors. Professor Zhu Baoqing from the School of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology offered critical guidance on the research topic and methodology. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the paper.
The research received financial support provided by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (BLX202333), China National University Student Innovation & Entrepreneurship Development Program (202410022068), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31770769) and National XA Science and Technology innovation project (2022XACX1100).
MV&AI Laboratory, established by Professor Yan Lei, specializes in intelligent robotics, smart detection technologies, and micro/nano-manufacturing equipment. The team boasts a strong foundation in mechanical design, hardware engineering, control systems, software development, and AI algorithm innovation. In recent years, they have led over 10 national and provincial-level projects, including grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation, and have collaborated on more than 20 industry projects. The lab has developed over 30 production lines and equipment systems, with research findings published in leading journals such as Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, Food Chemistry, and Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical.
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141999
Written by Liu Quancheng, Fan Shuxiang
Translated by Song He
Reviewed by Yu Yangyang










