Latest news
Recently, top journal IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy (TSTE for short, IF=8.8) published the paper entitled "Financial Incentives for Energy Resource Investments in Stochastic Economic Dispatch" by Wang Su, a youth scholar from the School of Information Science and Technology. Beijing Forestry University is the first completed unit.
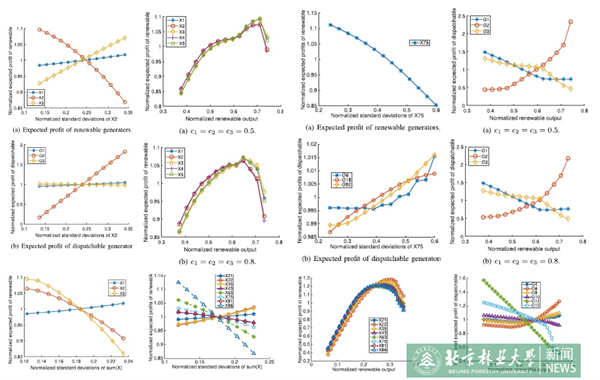
With deeper penetration of renewable supply, the deterministic conventional economic dispatch (CED) becomes inefficient due to less accurate forecasts. The key drawback of CED is to ignore the variation of real-time supply and demand from the point forecast. To address this problem, the literature has been discussing adjustments to deterministic market designs under high uncertainties. In addition to new market products and robust designs, stochastic designs have been studied as a promising direction. The stochastic economic dispatch (SED) is proposed to use a two-stage stochastic program, where the uncertain parameters, e.g., renewable generations, are characterized through a finite set of plausible scenarios and their corresponding probabilities. Thus, the SED makes day-ahead decisions while explicitly recognizing what real-time adjustments are required for all considered possible scenarios. Compared to the CED, the SED leads to a lower expected system cost, with additional consideration of real-time balancing costs and flexibility resource capacities.
SED provides a promising solution for short-term cost-efficiency with high renewable penetration. However, the long-term efficiency of SED, i.e., promoting efficient investments in both flexibility resources and renewable generations, has rarely been studied. Wang Su theoretically revealed the financial incentives for efficient investments in SED from both perspectives of the short-term and long-term performances: 1) the rationality behind the short-term failure of cost recovery or revenue adequacy was demonstrated, which provides proper signals to corresponding dispatchable generators, renewable generators, or system operator for long-term reconstruction and installation. 2) Through theoretical analysis of the statistical properties, it is proved that the long-term expected profits of renewable and dispatchable generators provide appropriate signals to guide their future investments. In conclusion, the SED can indeed motivate the investments of flexibility resources and renewables to match up better with each other in the network, benefiting the system efficiency and reliability in the long run. Simulations are conducted for validation.
Adjustments to current market structures are important for integrating renewable resources into the grid. The SED is a promising alternative to replace the CED. In this paper, the financial incentives for energy resource investments is theoretically recognized, verifying the long-term efficiency of SED. Not only the potential short-term failure of cost recovery and revenue adequacy but also the expected profits in statistics provide appropriate signals to incentivize the reconstruction and installation of both flexibility resources and renewable generations, benefiting the system efficiency and reliability in the long run.
Paper link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10038544












