Latest news
Recently, the research group of Professor Zhang Shuangbao of the School of Materials Science and Technology has published a paper entitled "Advanced Functionalized Materials Based on Layer-by-Layer Assembled Natural Cellulose Nanofiber for natural cellulose Electrodes: A Review " on a top journal Small (IF=13.3) in the field of materials.
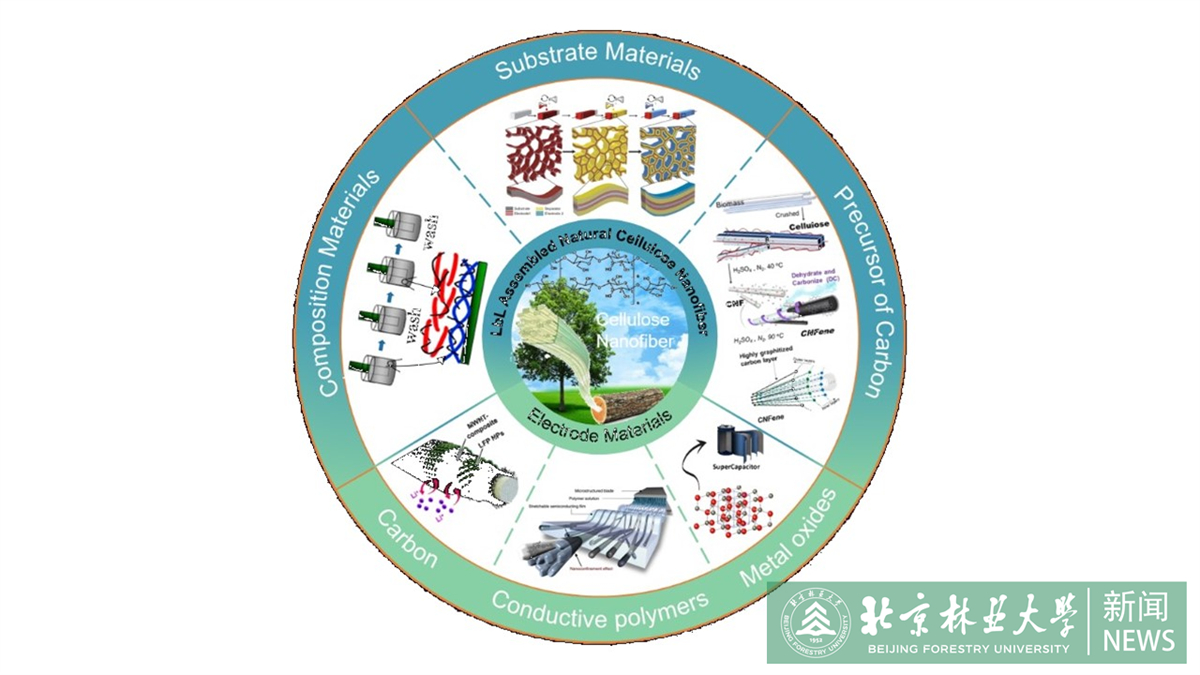
Energy is critical for the scientific progress and economic growth of human societies. The consumption of fossil fuels and the resulting impact on the environment makes it vital to develop sustainable energy resources, as well as the technologies of renewable energy storage and conversion systems. The incorporation of sustainable materials in the fabrication of energy storage devices is of paramount importance for advancing green energy development, as it fosters a reduction in the environmental footprint associated with energy production and storage.
The depletion of fossil fuel resources and its impact on the environment provide a compelling motivation for the development of sustainable energy sources to meet the increasing demand for energy. Accordingly, research and development of energy storage devices have emerged as a critical area of focus. The electrode materials are critical in the electrochemical performance of energy storage devices, such as energy storage capacity and cycle life. Cellulose nanofiber (CNF) represents an important substrate with potentials in the applications of green electrode materials due to their environmental sustainability and excellent compatibility. By utilizing the layer-by layer (LbL) process, well-defined nanoscale multilayer structure is prepared on a variety of substrates. In recent years, increasing attention has focused on electrode materials produced from LbL process on CNFs to yield electrodes with exceptional properties, such as high specific surface area, outstanding electrical conductivity, superior electrochemical activity, and exceptional mechanical stability. This review provides a comprehensive overview on the development of functional CNF via the LbL approach as electrode materials.
The first author of the paper is Du Keke, a Ph.D. candidate majoring in Wood Science and Technology at the College of Materials Science and Technology, and the corresponding author is Professor Zhang Shuangbao. Beijing Forestry University is the signature unit of the first author. This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32171707) and Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 6202024).
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202304739












