Latest news
Recently, the research group of Professor Chen Zhibo of the School of Information Science and Technology and the research team of the College of Forestry made progress in the research on the interpretability of the recognition of the vibration signal of dry moth pests. Pest Management Science published the research result entitled "The interpretability of the activity signal detection model for wood-boring pests Semanotus bifasciatus in the larval stage".
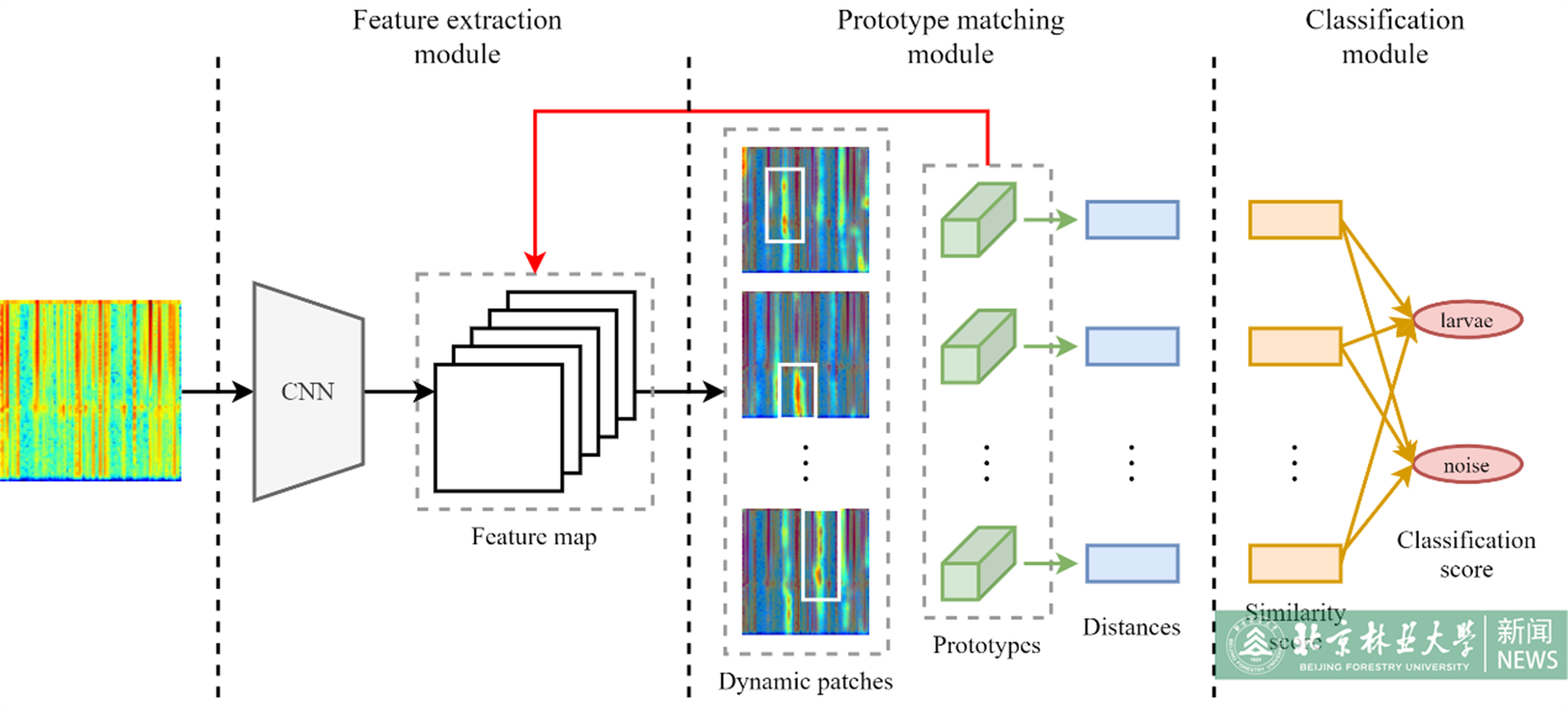
The acoustic detection model of activity signals based on deep learning could detect wood-boring pests accurately and reliably. However, the black-box characteristics of the deep learning model have limited the credibility of the results and hindered its application. Aiming to address the reliability and interpretability of the model, this paper designed an active interpretable model called Dynamic Acoustic Larvae Prototype Network (DalPNet), which used the prototype to assist model decisions and achieve more flexible model explanation through dynamic feature patch computation.In the experiments, the average recognition accuracy of the DalPNet on the simple test set and anti-noise test set for Semanotus bifasciatus larval activity signals reached 99.3% and 98.5%, respectively. The quantitative evaluation of interpretability was measured by the relative area under the curve (RAUC) and the cumulative slope (CS) of the accuracy change curve in this paper. In the experiments, the RAUC and the CS of DalPNet were 0.2923 and −2.0105, respectively. Additionally, according to the visualization results, the explanation results of DalPNet were more accurate in locating the bite pulses of the larvae and could better focus on multiple bite pulses in one signal, which showed better performance compared to the baseline model.The experimental results demonstrated that the proposed DalPNet had better explanation while ensuring recognition accuracy. In view of that, it could improve the trust of forestry custodians in the activity signals detection model and aid in the practical application of the model in the forestry field.
The first author of the article is Liu Xuanxin, a 2019 doctoral student in the School of Information Science and Technology, the corresponding author was Professor Chen Zhibo, and Beijing Forestry University was the only completed unit. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China Project (32071775).
Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.7566










